Material:Stainless Steel
Diaphragm pump: 0-120L/h ,7bar
Control box:Time relay 0-22h
Suction filter:PVC
Pressure relief valve:7bar
Shut-off valve:¼"connection

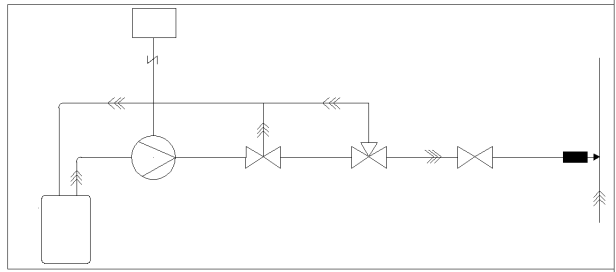
The cleaning system consists of a pump unit, a dispensing manifold, a control box, valves, and nozzles. The pump unit draws formic acid from the vessel and sends it through the dispensing manifold to the nozzles, which spray formic acid into the risers (Figure 2-1). The pump operation time is set by the control box and the aeration units are cleaned one by one.
The cleaning system can be a stationary or mobile unit. The mobile unit is mounted on a cart for easy transportation.
The stationary system can be operated automatically if required. Acid addition can be regulated by a loading solenoid valve, which is controlled by a timer that regulates the number of valve openings. Similarly, the start-up and regulation of the system can be automatically controlled by changes in back pressure.

Observe back pressure to determine when the aerator should be cleaned. Check back pressure periodically and record observations in the WWTP records. Back pressure must always be measured at a constant airflow rate or at a known air flow rate.
Due to the availability of SSI's cleaning system, it is recommended that the aerators be cleaned frequently or whenever the back pressure rises to 20 mbar. Cleaning intervals are plant-specific and can range from one week to one year depending on local conditions.
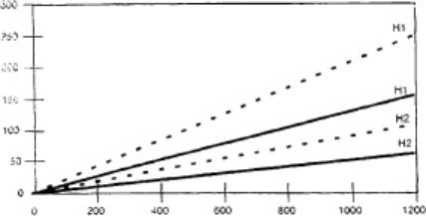
Adjustment of pump feed rate
The pump feed rate is determined by the size and airflow rate of the aeration unit to be cleaned and the amount of acid supplied. Figure 4-1 shows the required acid pumping rate (l/h) for different-sized aeration units at different air and acid supply rates.
Contact: Miss.Amber
Phone: 0086-18019736003
E-mail: amber@shdubhe.com
Whatsapp:0086-18019736003
Add: Room 428, No.255 Xinjinqiao Road, Pudong District, Shanghai, China
We chat
